What kind of fabric is flannel?
Flannel fabric has become extremely popular as clothes that are comfortable become...


Crepe fabric is one of the most loved textiles in modern fashion. Designers value it for its soft drape, elegant texture, and versatility across casual and formal wear. For fashion startups, designers, and sourcing managers in the USA, understanding what crepe fabric is, how it is made, and where it comes from helps make better design and production decisions.
According to Statista, the global synthetic fibers market, which includes polyester-based crepe fabric, was valued at approximately USD 63.9 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach around USD 93 billion by 2030, driven by strong demand from apparel brands and private labels, especially in the United States.
This guide explains crepe fabric in clear terms: from its properties and manufacturing process to its uses, advantages, and limitations. So, you can decide if crepe material is right for your next collection.
Crepe fabric is a textile recognized for its slightly wrinkled, crinkled, or pebbled surface, which is created through special yarn twisting or finishing techniques. This distinctive texture gives crepe its signature appearance and a soft, fluid movement. Unlike flat woven fabrics, crepe textiles have a gentle bounce and natural drape that allows garments to move smoothly with the body, making it both visually appealing and comfortable to wear.
Crepe material can range from very lightweight to medium weight, depending on the fiber used and how it is constructed. This wide range makes crepe suitable for both delicate fashion pieces and more structured apparel.
Crepe fabric is valued for several defining characteristics:
These characteristics of crepe cloth make it a popular choice for garments that require elegance without heaviness.
Crepe fabric can be produced using both natural and synthetic fibers, including:
This fiber flexibility allows brands to choose crepe material based on budget, performance requirements, sustainability goals, and end-use application.
Designers favor crepe fabric because it:
These qualities make crepe fabric a reliable and creative option for modern apparel collections across multiple fashion segments.
Understanding crepe fabric properties helps brands select the right type for each garment category.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight to medium weight |
| Breathability | High in silk, cotton, rayon; lower in polyester |
| Drape | Fluid and elegant |
| Stretch | Slight natural give (more with stretch crepe) |
| Texture | Crinkled or pebbled surface |
| Wrinkle resistance | Better than many flat fabrics |
| Hand feel | Soft, smooth, and flexible |
| Durability | Depending on fiber type |
| Lightweight crepe vs heavy crepe options allow designers to use the same fabric family across seasons and collections. | |
Many buyers ask, how is crepe fabric made? The process combines fiber choice, yarn twisting, and finishing techniques to create its unique texture.
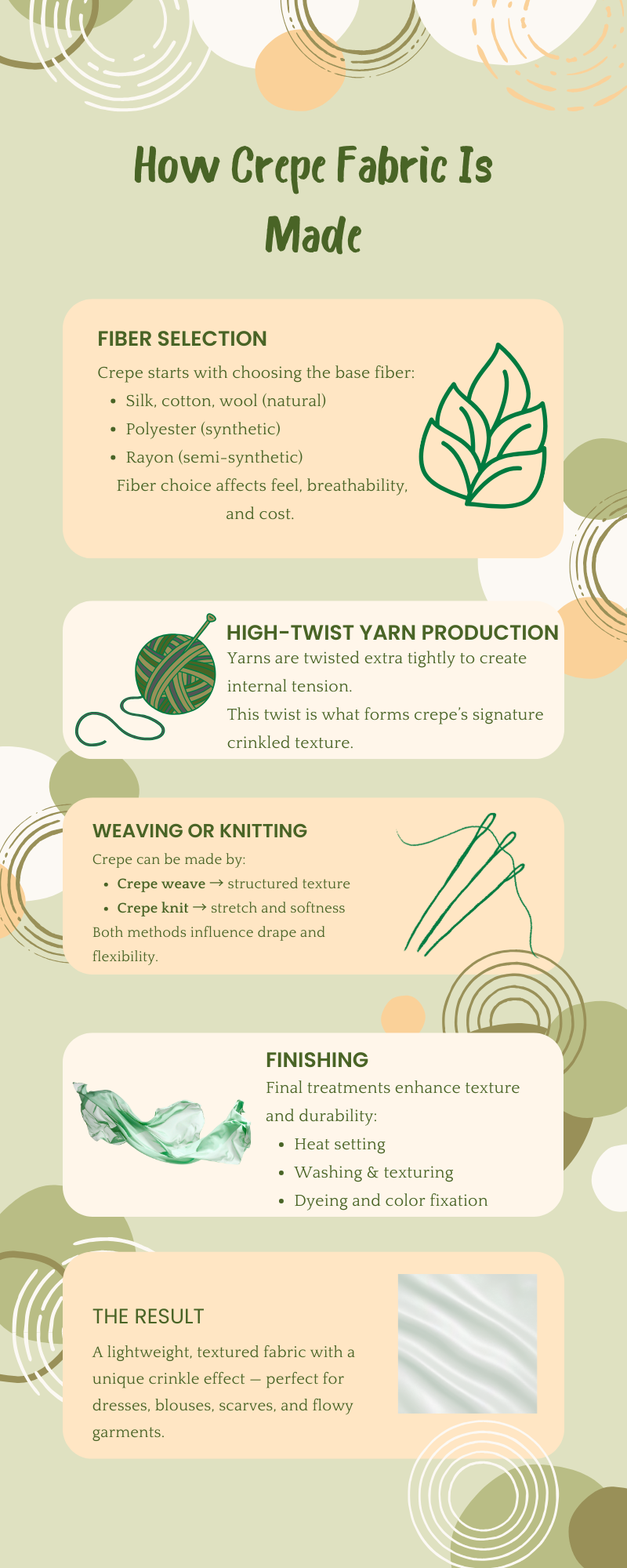

The process starts with selecting fibers:
This step determines breathability, cost, and end use.
High-twist yarns are the heart of crepe fabric. The yarns are twisted more tightly than standard yarns. When released or finished, the tension creates the crinkled texture crepe is known for.
Crepe can be produced using:
Woven crepe offers structure, while knit crepe provides flexibility.
Final finishing enhances texture and performance:
This explains how crepe fabric is produced at an industrial level.
Understanding where crepe fabric comes from adds important context to its value, quality perception, and continued relevance in modern fashion. Crepe’s origins are deeply tied to traditional textile craftsmanship and the evolution of luxury fabrics.
The history of crepe fabric traces back several centuries and spans multiple regions:
In its early use, crepe was primarily made from silk and often reserved for formal and ceremonial garments. Its soft drape and unique texture symbolize elegance, refinement, and status, especially in luxury apparel.
Today, crepe fabric production is fully globalized to meet growing demand from fashion brands worldwide.
Major manufacturing hubs include:
Modern production focuses on polyester crepe, which dominates large-scale manufacturing due to its cost efficiency, consistency, and ease of care. At the same time, silk crepe continues to hold a premium position in luxury and designer markets, valued for its natural feel, breathability, and timeless appeal.
There are many types of crepe fabric, each made with different fibers, weights, and finishes. These variations allow designers and apparel brands to choose the right crepe material based on garment function, target market, and price point. Below are the most common crepe fabric types used in fashion and apparel production.
Crepe de Chine is one of the most popular crepe fabrics. Traditionally made from silk and now widely available in polyester versions, it has a smooth surface with a subtle texture and excellent drape. It feels lightweight and soft, making it ideal for blouses, dresses, skirts, and flowing tops. Crepe de Chine works well for both everyday wear and elevated fashion pieces.
Georgette crepe is a lightweight and sheer crepe fabric with a more pronounced grainy texture. It has a slightly crisp feeling while still offering fluid movement. This type of crepe fabric is commonly used for scarves, layered garments, feminine dresses, and modest fashion. It is often made from silk or polyester and is valued for its airy appearance.
Wool crepe is heavier and more structured than lightweight crepe fabrics. It has a refined texture and excellent drape while maintaining shape, making it suitable for tailored garments. Wool crepe is often used for trousers, skirts, blazers, and suits, especially in cooler seasons. It is known for durability and a polished look.
Polyester crepe is one of the most widely used crepe textiles in mass production. It is affordable, wrinkle-resistant, and easy to care for. While it is less breathable than natural fiber crepe, it offers consistency and durability, making it ideal for everyday dresses, workwear, and ready-to-wear collections aimed at larger markets.
Stretch crepe is made by blending crepe fibers with elastane or spandex. This type provides added flexibility and comfort while maintaining the classic crepe texture. Stretch crepe is commonly used for fitted dresses, body-skimming silhouettes, jumpsuits, and performance-inspired fashion pieces where movement is important.
Plissé crepe features intentionally pleated or crinkled surfaces that add dramatic texture and visual depth. It is usually made from polyester and treated through heat-setting processes. Plissé crepe is popular in fashion-forward designs, statement garments, and contemporary collections where texture plays a key role.
Satin crepe combines two textures in one fabric: smooth, satin finish on one side and a crepe texture on the other. This dual-surface fabric offers versatility and elegance, making it suitable for evening dresses, bridal wear, and formal garments. Satin crepe provides a balance between shine and structure.
French crepe is a lightweight, high-quality crepe traditionally made from silk. It has a soft hand feel, elegant drape, and refined texture. This type of crepe fabric is commonly used in luxury fashion and designer collections where premium materials are required.
| Type | Fiber | Weight | Drape | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crepe de Chine | Silk / Polyester | Light | Soft | Blouses, dresses |
| Georgette Crepe | Silk / Polyester | Light | Flowing | Scarves, layering |
| Wool Crepe | Wool | Medium | Structured | Trousers, suits |
| Polyester Crepe | Polyester | Light–Medium | Stable | Everyday wear |
| Stretch Crepe | Blends | Medium | Flexible | Fitted garments |
| Plissé Crepe | Polyester | Light | Textured | Statement pieces |
| Satin Crepe | Silk / Polyester | Medium | Smooth-back | Evening wear |
| French Crepe | Silk | Light | Elegant | Luxury apparel |
This wide range of crepe fabric types allows apparel brands to apply crepe across different collections, seasons, and customer segments while maintaining consistency in look and performance.
Knowing the advantages and disadvantages of crepe fabric helps brands plan better collections.
| Feature | Silk Crepe | Polyester Crepe |
|---|---|---|
| Feel | Luxurious, soft | Smooth, stable |
| Breathability | High | Moderate |
| Cost | High | Affordable |
| Care | Delicate | Easy |
| Sustainability | Natural fiber | Synthetic |
Crepe fabric uses span many apparel categories:
Its versatility makes crepe material a staple for fashion brands.
Proper care protects garment quality and lifespan.
Care instructions should always match the fiber type.
To decide what is crepe material best for your brand, consider:
Lightweight crepe works well for summer collections, while heavy crepe suits tailored or transitional styles.
Choosing the right production partner matters as much as choosing the right fabric. SEAM Apparel supports fashion brands with custom crepe fabric sourcing, pattern development, and scalable production. From sampling to bulk manufacturing, our team helps turn designs into market-ready garments.
Brands looking for reliable private label production, women’s wear manufacturing, and expert fabric guidance benefit from collaborating with experienced professionals who understand both design and manufacturing requirements.
Crepe fabric remains a timeless textile due to its texture, drape, and adaptability. By understanding what crepe fabric is, its properties, manufacturing process, and uses, fashion brands can make confident decisions that align with quality, cost, and customer expectations.
For designers and apparel startups in the USA, crepe textiles continue to offer creative freedom and commercial value across fashion categories.